Resources
General Writing Tips
Modern Language Association (MLA) 9th Edition, 2021
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) 17th Edition, 2017
American Psychological Association (APA)
APA Citation Style Quick Tips
Below are helpful resources for completing your writing assignments. You can also browse the official American Psychological Association website for guides, examples, and other information about APA style.
Title page overview
In APA 7 professional title pages and student title pages have different formatting. For students the title page should include the following:
Title Of Paper
Author’s Name
Institutional Affiliation
Course number and name
Instructor name
Assignment due date
Page Header
A “page header” is also known as a “running head” and should be included at the top of every page and should only include the page number flush to the right for student papers.
Professional papers will also include the paper title as a “running head” which is a shortened version of no more than 50 characters flush left using all capital letters.
Abstract
On the second page you will have the word “Abstract” centered and on the next line you should include a concise summary of your research. The summary should include your research topic, research question(s), methods, results, and data analysis. In some instances, you can also include suggestions for what your research implies about the topic. After the summary, you should include your keywords under the paragraph. The word and the colon that follows should be italicized but your keywords should be in normal case.
Information Adapted From:
Purdue Online Writing Lab. (n.d.). General Format. Purdue Online Writing Lab. https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/general_format.html
Getting Started with APA (PDF)
For In-Text Citations APA requires:
- the author’s last name
- the year of publication
- the page numbers
A Quick Guide to APA Source Usage (PDF)
If the author is introduced before the quotation, then the year will follow the author’s name in parentheses and in the citation at the end of the sentence you only need to include a page number indicated it “p.”
Salem (2016) found that a student's environment before arriving at the university determines whether they will use the writing center (p. 148).
If there is no signal phrase, or the signal phrase does not include the author's part and name then all three components are needed at the end of the sentence in parenthesis with commas between each “p.” before the page numbers.
A surprising finding is that student’s environment prior to attending college or university determines if they will use the writing center services (Salem, 2016, p.148).
With a signal phrase:
Giaimo et al. (2018) state that while writing centers are a large and important data collection source there is no easy way to analyze this data (p. 225).
Without a signal phrase:
Writing centers are often a site with various means of data collection, however, there is not an easy way to analyze this data (Giaimo et al., 2018, p. 225).
If there is no author listed, use a shortened title (note: use the full title if it is short) around the title or abbreviated title.
Example: (“Deserving of Exoneration,” 2016) and use double quotations
If no page number, use paragraph numbers and use the abbreviation “para.” and the number in parenthesis.
Example: As Miller states (2004, para. 6) ....
Paraphrasing refers to rewriting a given sentence using your own words. When we need to use a sentence in our writing that someone else wrote, we paraphrase it. That is, we use the same idea(s) in that sentence and write it differently. In addition to using different words, we use different grammar. The main purpose of paraphrasing has to do with being able to use someone else’s ideas while we write our own texts. Of course, it is required that any writer acknowledges the original source using the proper citation format.
A summary should be a short version of a longer original source. Its main goal is to present a large amount of information in a short and concise text that includes only the most important ideas of the original text.
When paraphrasing or summarizing, first introduce the author and then present their ideas. Follow this discussion with an explanation of how the source relates to your argument.
When reading a passage, try first to understand it as a whole, rather than pausing to write down specific ideas or phrases. Think of what "your own words" would be if you were telling someone who's unfamiliar with your subject (your mother, your brother, a friend) what the original source said.
When you directly quote an author, you must follow-up the quote with a discussion of how it is connected to your main ideas. Without explanation, the quotes intended purpose is lost on the audience.
When to quote?
Deciding whether you should paraphrase or directly quote a source can be difficult. In general, you should only directly quote a source when preserving the author’s language is important.
Secondary sources are documentswhose author(s) did not participate in the events or study that they are reporting on. A secondary source typically analyzes primary sources.
To synthesize is to compile the information you have researched from various sources and present them in a cohesive format thatmakes connections between sources. The purpose of a synthesis is to establish an understanding of a subject based on information gathered from various sources and to show how these sources can be combined to present a clearer understanding of the topic.
- The label “DOI” is no longer needed and DOI’s should be presented as URLs.
- No longer need to use label “Retrieved from” before URLs
- The location of a source’s publisher is no longer needed
- The format of an eBook is no longer needed.
Author Last name, Firstinitial. (Year of publication). Title of book. Publisher.
Author Last name, Firstinitial. (Eds.). (Year of publication). Title of book. Publisher.
Author Last name, Firstinitial. (Year). Title of article. In Editor First Initial. Last Name (Ed.), Title of book (page range). Publisher. DOI or URL (if applicable)
Author Last name, Firstinitial. (Year). Title of article. In Editor First Initial. Last Name (Ed.), Title of book (page range). Publisher. DOI or URL (if applicable)
Author last name, first initial. (Year). Title of article. Name of Periodical, Volume(issue number), Page number or range. DOI or URL.
Author Last name, Firstinitial. (Year). Name of the article. In Editor Name (Ed.), Title of encyclopedia/larger work (Edition). Publisher Name. URL
Author Last name, Firstinitial. (Date of publication and/or last modification). Title of document. Site Name. URL
Director, D. D. (Director). (Date of publication). Title of motion picture [Film]. Production company.
Person or group who uploaded video. (Date of publication). Title of video [Video]. Website host. URL.
Photographer, P. (Year of publication). Title of photograph [Photograph]. Source. URL.
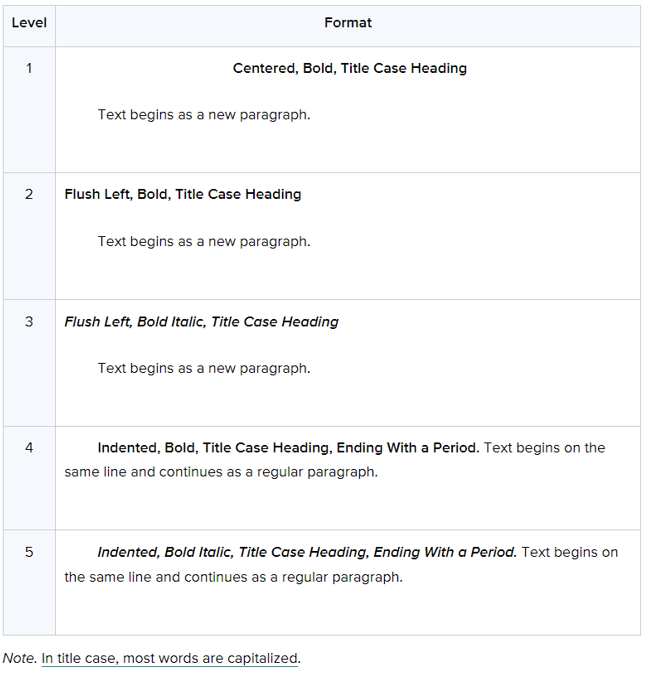
Headings are used to identify different sections of a paper.
- Headings should be: Descriptive, Concise, and Clearly Worded
Headings should follow the following formatting rules based on level:
Workshops and Events
Check back soon!


