 |
Stockton's Regeneration Project |
|
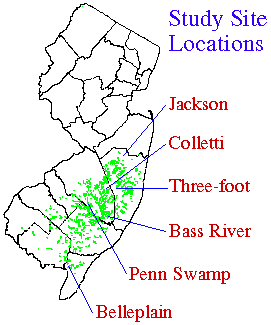 |
This site is located on the New Jersey Forestry Resource Center property (also known as the State nursery). The experiment is converting a swamp-hardwood stand back to white-cedar. The site has two treatments; an electric fence plus herbicide, and herbicide only. Both treatments were sown with cedar seed in 1991. An additional experiment with cedar seedlings and cuttings protected by plastic deer collars was added by Dr. Kuser from Rutgers University in 1992. The site is reproducing to cedar successfully. The site was given back to the State in 1996 and other experiments have been started there.
Treatments and Dates:
|
![]() More photos from the Jackson site.
More photos from the Jackson site.
Results | Discussion / Conclusions
The Colletti site is located in Lebanon State Forest. It was a cedar stand clearcut in 1985 that did not regenerate itself for five years. In 1990, it became part of the regeneration study. Arsenal was aerially applied on all but one (control) area. Additional treatments include a five-strand solar powered electric fence, and routine sprayings with Hinder, a deer repellant. The site, particularly the area within the electric fence, has reproduced successfully. The difference in cedar reproduction in & out of the electric fence is dramatic. The site has been maintained, the electric fence was 'pulled back' in 1999 to allow an acre or two to be exposed to the deer to see their effect at this late date. The site is being remeasured for the 2000 year growth and will be measured again in 2010.
![]() More photos from the Colletti site.
More photos from the Colletti site.
Results | Discussion / Conclusions
The Three-foot site, added later in the study, is located in Stafford Forge, in the Bass River State Forest. The site was illegally logged over a period of years severely depleting the white-cedar. The entire area was surrounded with a five-strand solar powered electric fence and half of the enclosed area was herbicided with Arsenal (in 1992 and 1993). The white-cedar have regenerated at the highest density recorded on any study site: a 'carpet' of cedar averaging greater than three million per hectare! The site is being remeasured for the 2000 year growth and will be measured again in 2010.
![]() More photos from the Three-foot site.
More photos from the Three-foot site.
Results | Discussion / Conclusions
The Penn Swamp site was the last state clearcut of cedar. Part of the swamp was clearcut from 1989 to 1991. All but a small area of the clearcut was enclosed by a twelve-foot high woven mesh wire fence. Inside and outside the fence, a series of logging slash experiments were delineated in a Latin square design. The cedar have successfully regenerated inside the fence. The slash experiments have given strong counter-evidence about the effects of slash on long-term cedar reproduction and survival.The site has been remeasured for the 2000 year growth and will be measured again in 2010.
![]() More photos from the Penn Swamp site.
More photos from the Penn Swamp site.
Results | Discussion / Conclusions
This site is located on a larger upland pine clearcut performed in 1989. A part of this clearcut seemed to be wetter and previously possess some swamp hardwoods. It was decided to try to regenerate white-cedar by sowing cedar seed in an area enclosed by an electric fence. A clay lens under the site has perched the precipitation making the site wet enough to support high densities of cedar. Additional hydrologic work is being done on this fascinating site. A back fire was started in 1999 to prevent a larger fire from threatening nearby homes. part of the site was burned and the electric fence had to be rebuilt. The site is being remeasured for the 2000 year growth and will be measured again in 2010.
![]() More photos from the Bass River site. (190k)
More photos from the Bass River site. (190k)
Results | Discussion / Conclusions
Two sites were set up within a few miles of each other on the Belleplain State Forest in 1990. One site is next to a large upland clearcut which was to serve as a food-patch 'diversion' to deer. The other nearby site has no food-patch.
The Belleplain sites were upland-lowland transition forests of mostly oak, pine, and maple. These sites represented the driest areas we attempted to regenerate in the study. Drought during the study further complicated cedar regeneration attempts. Treatments consisted of electric fences, Hinder applications, artificial seeding, and plantings of cedar cuttings and seedlings. Results have been mixed, but many insights into factors limiting cedar regeneration have been uncovered. Both sites were given back to the State in 1995. Some more cutting of the residual cedar stand on the food patch site was done by the New Jersey Forest Service.
![]() More photos from the Belleplain sites.
More photos from the Belleplain sites.
Results | Discussion / Conclusions